test low impact insecticides|What can we learn from commercial insecticides? Efficacy, : maker Advantages to receiving reduced risk status for your registration action: 1. Expedited decision timeframe under the Pesticide Registration Improvement Act . See more O ISS® funciona como um sistema de suporte à metodologia de gestão do ISSQN, utilizando a como plataforma tecnológica. A solução de gestão proporciona o controle de documentos físicos e eletrônicos. . Município de Campina Grande/PB. Endereço: Av. Rio Branco, n° 304 - Centro - Campina Grande - PB – CEP: 58.400-058 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB11 de dez. de 2023 · Neste artigo, vamos explicar como ativar seu Bet7 bônus de boas .
The Office of Pesticide Program's Conventional Reduced Risk Pesticide Program expedites the review and regulatory decision-making process of conventional pesticides that pose less risk to human health and the environment than existing conventional alternatives. The goal of this program is to quickly . See more

Advantages to receiving reduced risk status for your registration action: 1. Expedited decision timeframe under the Pesticide Registration Improvement Act . See more Our human health risk assessments estimate the nature and probability of harmful health effects in people who may be exposed to pesticides: in the food and water they . One resource receiving little attention is the Pesticide Risk Tool (PRT), developed by the IPM Institute in Madison, WI. The PRT includes 15 indices and uses a probabilistic .Abstract. Laboratory bioassays have become increasingly important because of their predictive value, generating comparative toxicity data on many chemicals in relatively short times at .
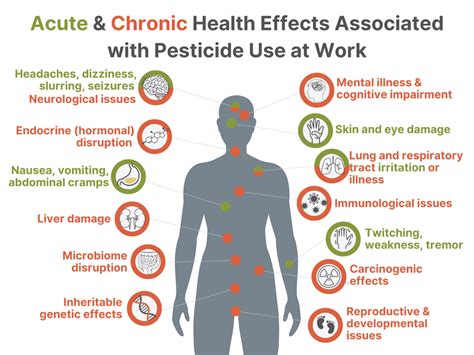
What are the potential health effects of pesticides? How does EPA determine what the effects of pesticides on humans are and whether they are acceptable? Where can I get .The respective toxicity tests for human health risk assessments required by EPA are (1) the acute toxicity test, which assesses the effects of short-term exposure to a single dose of .
Pesticides that are classified as highly toxic (Toxicity Category I) on the basis of either oral, dermal, or inhalation toxicity must have the signal words DANGER and POISON printed in red with a skull and crossbones . Pyrethroids are currently the most widely used insecticides by farmers, as they have low toxicity in mammals, low environmental impact, are effective against a wide spectrum .
Insecticides are very toxic to all aquatic arthropods, particularly to zooplankton and insect larvae [124,125]. Residues of insecticides in streams are at higher levels and more common near .
There is a growing list of insecticide classes; pyrethroids remain the principal insecticide used in bednets but recently, novel non-pyrethroid IRS products, with contrasting . By creating a low genetic diversity population SF-IsoA, we were able to test the hypothesis that reduced genetic diversity may (i) reduce the variability of insecticide response estimates (i.e. LD 50 values) within the population and increase repeatability, and (ii) genetically fix the strain and obtain a stable reference population through . To determine risk, one must consider both the toxicity or hazard of the pesticide and the likelihood of exposure. A low level of exposure to a very toxic pesticide may be no more dangerous than a high level of exposure to a relatively low toxicity pesticide, for example. On this page: What are the potential health effects of pesticides?
Hazards of pesticides to bees – 10th International Symposium of the ICP-Bee Protection Group 86 Julius-Kühn-Archiv 423, 2009 Phacelia tanacetifolia was used a model crop because it is highly . Find out about the Conventional Reduced Risk Pesticide Program, which expedites the review and regulatory decision-making process of conventional pesticides that pose less risk to human health and the environment than existing conventional alternatives. . Low impact on human health. Lower toxicity to non-target organisms (birds, fish, plants . When people come into contact with large quantities of pesticide, the result may be acute poisoning or long-term health effects that may include cancer and adverse effects on reproduction. Scope of the problem. Pesticides are among the leading causes of death by self-poisoning, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Low concentrations of insecticides have indirect consequences on non-target members of the community across the multiple trophic levels, and the indirect insecticide-mediated effects are generalized across two geographically distinct amphibian assemblages (Hua and Relyea 2012). Tadpoles were killed and growth abnormalities were observed, when .
Control of insect pests has long relied on pesticide-based interventions. It is not surprising that, as the intensity and geographic spread of chemical control increases, insects have developed . Ecotoxicological impact of dinotefuran insecticide and its metabolites on non-targets in agroecosystem: Harnessing nanotechnology- and bio-based management strategies to reduce its impact on non-target ecosystems . These low molecular weight and high-water solubility of dinotefuran exacerbate the issue of environmental contamination. The .The findings will be of interest to those considering the wider impact of neonicotinoid pesticide use when assessing their future use in agricultural environments. . (t test, p ≤ 0.05, n = 13 and n = 17 for 0.25 and 0.50 mg/seed, . Honeybees collected low levels of crop pollen, and higher levels of neonicotinoid contamination were found . We determine the effects of a pesticide after prolonged and repeated exposures. Chronic effects (non-cancer) Carcinogenicity (cancer) Developmental and Reproductive Testing: Identify effects in the fetus of an exposed pregnant female (birth defects) and how pesticide exposure affects the ability of a test animal to successfully reproduce.
The toxicity of a particular pesticide is determined by subjecting test animals to varying dosages of the active ingredient (a.i.) and each of its formulated products. . The key to reducing health hazards when using pesticides is to always limit your exposure by wearing PPE and use a low-toxicity pesticide when available. Reading the label . The use of synthetic insecticides has been a solution to reduce mosquito-borne disease transmission for decades. Currently, no single intervention is sufficient to reduce the global disease burden caused by mosquitoes. Problems associated with extensive usage of synthetic compounds have increased substantially which makes mosquito-borne disease .
2.1. General protocol. To assess the impact of flupyradifurone and poor nutrition on both sucrose responsiveness (experiment 1) and long-term memory (experiment 2) we used a modified version of a free-moving proboscis extension reflex protocol [[38,65,66]].Six bumblebee (B. impatiens) colonies (four for experiment 1 and two for experiment 2) were purchased (Koppert Biological .Other bioinsecticides may have low impact on pollinators due to their low toxicity or short residual, which allows them to be applied in the evening or at dawn when bees are inactive. Considerations for Using Certain Biopesticides. The following active ingredients are found in products that have minimal impact on bees and other beneficial insects. Unlike the majority of synthetic insecticides that induce neurotoxicity in pests, biopesticides exhibit diverse modes of action like anti-feeding, mating disturbance, desiccation, and suffocation [].Biopesticides, thus, have a great potential to act as a good alternative to synthetic pesticides [].Moreover, the marketing and commercialization of biopesticides can be . 2. Considerations regarding volumes of insecticide formulations. Due to the emphasis and reliance on insecticide applications, it is worthwhile briefly reviewing some of the basic considerations regarding volume of .
Insecticide resistance. The overall mortality of An. gambiae s.l. in the 24 h following exposure to the diagnostic dose (DD) of deltamethrin was 23.33% [95% CI 14.63–32.05%], indicating a .
What can we learn from commercial insecticides? Efficacy,
Because most insecticides would have returned a value of 1 (or 100% probability of impact on pollinating insects), the risk scale had to be expanded to allow for comparisons among insecticides. For many of the environmental indices, the probability of impact was calibrated against field data and the risk scores are therefore very real and not . Methods: A series of experiments were conducted in the WHO tunnel test to evaluate the impact of the following factors on bio-efficacy endpoints of mosquito mortality at 24-h (M24) and 72-h (M72) and blood-feeding success (BFS): (1) baits (rabbit, membrane, human arm); (2) exposure time in the tunnel (1 h vs. 12 h); and (3) mosquito density (50 .
Estimates suggest that global pesticide use grew 20% over the last decade and by 153% in low-income countries, specifically. 1 Organophosphate pesticides are one of the most extensively applied insecticides in the field of agriculture. 2 Approximately 40% of all pesticides produced and used commercially belong to this category. 2 Pesticides . The ideal insecticide should show high efficacy to target and low toxicity to non-target organisms. Unfortunately, it is seldom possible. The effects of low, sublethal concentrations of . We asked if and how a neonicotinoid pesticide affects free-flying bees’ ability to learn about floral features, which allowed us to consider how acute exposure might impact not only the ability .
Background Malaria is one of the most devastating tropical diseases, resulting in loss of lives each year, especially in children under the age of 5 years. Malaria burden, related deaths and stall in the progress against malaria transmission is evident, particularly in countries that have moderate or high malaria transmission. Hence, mitigating malaria spread requires .
The lower the LD 50 or LC 50 of a pesticide product, the greater its toxicity to humans and animals. Pesticides with a high LD 50 are the least toxic to humans if used according to the directions on the product label. The chronic toxicity of a pesticide is determined by subjecting test animals to long-term exposure to the active ingredient. The pesticide law requires us to use an extra 10-fold safety factor, if necessary, to protect infants and children from effects of the pesticide. Risk Equation. The risk to human health from pesticide exposure depends on both the toxicity of the pesticide and the likelihood of people coming into contact with it. Simply put, RISK = TOXICITY x . Insecticide resistance across sub-Saharan Africa may impact the continued effectiveness of malaria vector control. We investigated the association between carbamate and pyrethroid resistance with . Physiological resistance and behavioral responses of mosquito vectors to insecticides are critical aspects of the chemical-based disease control equation. The complex interaction between lethal, sub-lethal and excitation/repellent ('excito-repellent’) properties of chemicals is typically overlooked in vector management and control programs. The .

vochtmeters muren

みんながダウンロード保存した人気のTwitter動画 | TWIVIDE.
test low impact insecticides|What can we learn from commercial insecticides? Efficacy,